Obesity and Bariatric Surgery Facts, Statistics and Rates of Obesity

Obesity is a disease that affects 34 percent of adults age 20 and over in the United States, which amounts to more than 72 million people. About 32.2 percent of American men and about 35.5 percent of American women are obese.*
The number of overweight and obese Americans has increased almost continuously since 1960. About 68 percent of U.S. adults were estimated to be either overweight or obese by the 2007-2008 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
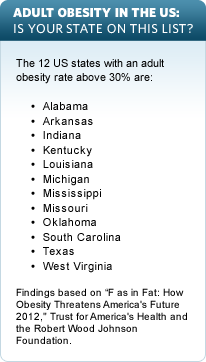
The rate of obesity differs from state to state, which is probably a reflection of various lifestyle, age and economic factors. The rankings below are based on data from 2008 to 2010.
Are You Obese?
A person is considered obese when his or her body mass index (BMI) is over 30 or weight is 20 percent or more above normal weight. “Morbid obesity” refers to being more than 100 pounds over normal weight or having a BMI of 40 or greater.
Causes of Obesity
If you are obese, you may have inherited it, because it has a strong genetic component. Your environment is another contributor. Our culture fosters the tendency toward obesity: physical activity isn’t often required in our society, and the foods that cost the least often contain the most calories and the fewest nutrients.
There are a number of dangerous consequences. Obesity increases your risk of developing high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke, gallbladder disease, age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and cancer of the breast, prostate, and colon. In fact, obesity increases your risk of death. And that’s not all. The lesser-known effects of obesity may also include asthma, pregnancy complications, infertility and even Parkinson’s disease, a progressive neurological disorder.
If maintained, even weight losses as small as 10 percent of body weight can improve your health.
Knowing the various reasons that people become obese can help you understand your own struggle more clearly.
Whether you decide to have weight loss surgery or not, understanding your condition is vital for losing weight and keeping the weight off. Here are the most common causes of obesity:
- Genetics – Obesity can often be traced to genes, and the brain can induce appetite tendencies.
- Illness – Hypothyroidism, Cushing Syndrome and depression.
- Psychology – Mental illness and emotional problems.
- Lifestyle habits – Poor diet and low levels of daily activity.
You may be able to lose weight and improve your health by addressing the causes of your obesity.
But sometimes these attempts do not work without surgery. If you have been losing the battle with obesity, it may be time to consider bariatric surgery. To help you make a decision, talk to a qualified bariatric physician and surgeon.
*Source: National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 2007-2008, conducted by National Center for Health Statistics (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)